SNCR – Selective Non-Catalytic Reduction
For the reduction of nitrogen oxides in the flue gas
In selective non-catalytic reduction (SNCR), urea reacts with harmful nitrogen monoxide and nitrogen dioxide from the flue gas to form harmless nitrogen and water.
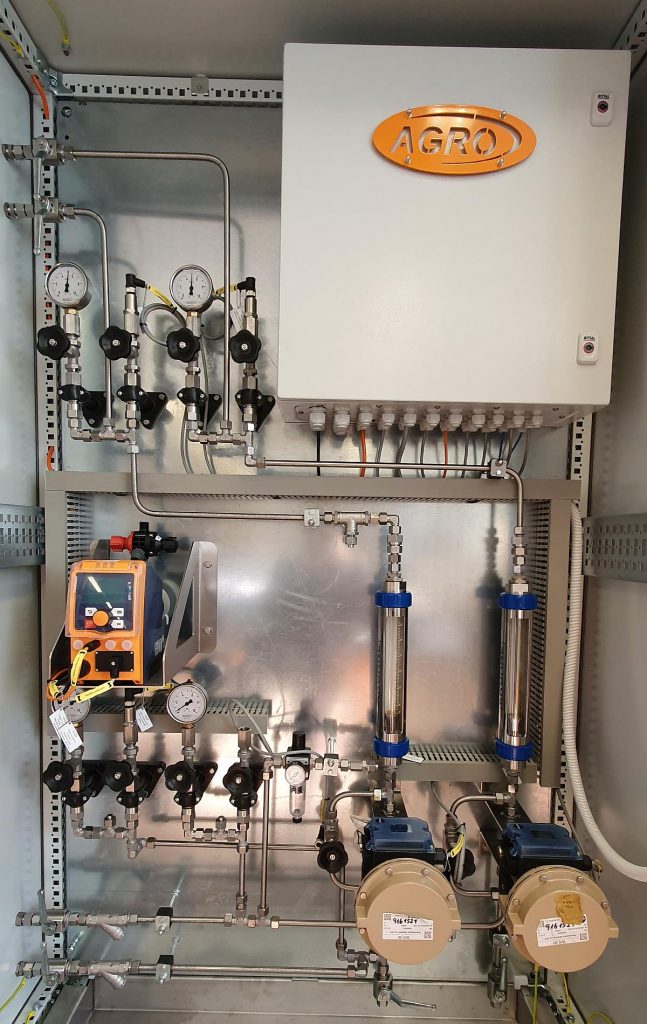
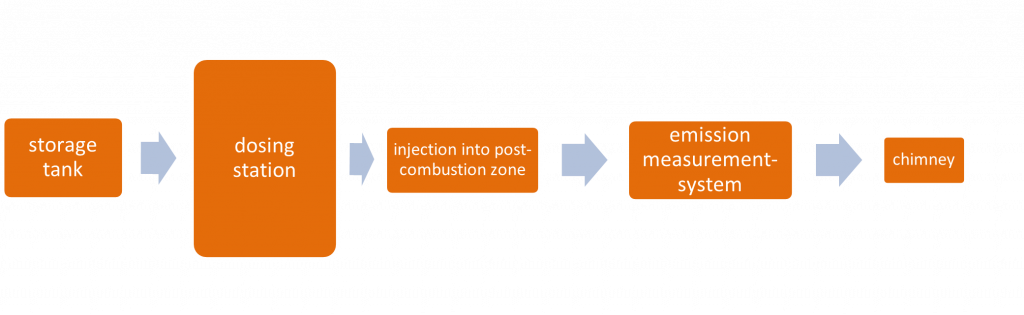
AGRO SNCR systems essentially consist of a tank storage system for the reducing agent and a dosing station with subsequent injection in the afterburning zone of the furnace. The required amount of reducing agent is calculated in advance depending on the boiler load and corrected on the basis of the measured NOx value.
The atomizing nozzles mix the reducing agent with the atomizing air. The nozzles are specially matched to the combustion chamber geometry to make optimum use of the reaction chamber.
With the installation of SNCR technology, a maximum reduction of NOx values of 70% from the initial value can be achieved at a combustion chamber temperature of 850–950°C and an output of 50–100%. The requirement of a reduction above 70% can be achieved with the integration of a catalyst.
You can find some of our references with an integrated SNCR system >> here.
Share post

Interested? – Contact us!
Get in touch with us – we will be happy to advise you on your plans and implement your projects!